Schedule
Book a telehealth appointment from wherever you are. No insurance necessary.
Achieve your weight-loss goals with GLP-1 treatments like Wegovy® and Zepbound®, guided by licensed providers every step of the way.
Personalized care for women, with HRT and lifestyle support to ease menopause symptoms and restore balance.
Simple, supportive mental health care on your terms, including access to prescription medication when appropriate.
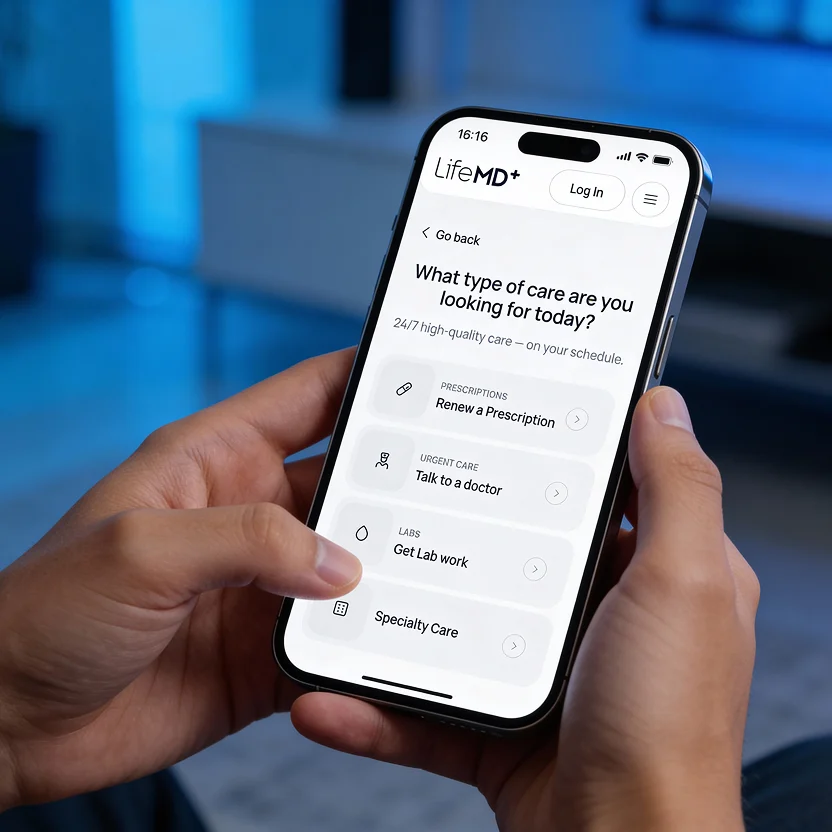
Care without the wait—connect 24/7 with licensed providers for same-day prescription refills and common concerns like colds, flu, rashes, and more.
Talk to a doctor anytime, anywhere — 24/7 urgent & primary care with a telehealth visit in under one hour.
Get your medication prescribed online and sent same-day to your local pharmacy for pickup.
Save time, money, and the hassle — no in-person visits or insurance required. Get immediate and long-term care 100% online.


Prescription treatments are tailored to your specific condition, ensuring effective relief.

Urgent evaluation is crucial to identify your condition early and prevent complications.
Accurate testing, if needed, can confirm your diagnosis and guide the best course of treatment

Licensed providers can send prescriptions to your local pharmacy within an hour, day or night.
step 1
Book a telehealth appointment from wherever you are. No insurance necessary.

step 2
Meet with a board-certified doctor or nurse practitioner from your mobile device.

step 3
Get a prescription if needed (save up to 90%), and pick it up at your pharmacy.
Many people experience acid reflux from time to time. This is when stomach acid backs up into the esophagus. But when acid reflux is severe or occurs multiple times a week, it may be diagnosed as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
Treatment for GERD may include prescription medications, which can help to reduce the amount of acid produced by the stomach. Since GERD can sometimes lead to serious complications, it's important to consult with a doctor if you frequently experience acid reflux.
Get Started Get Started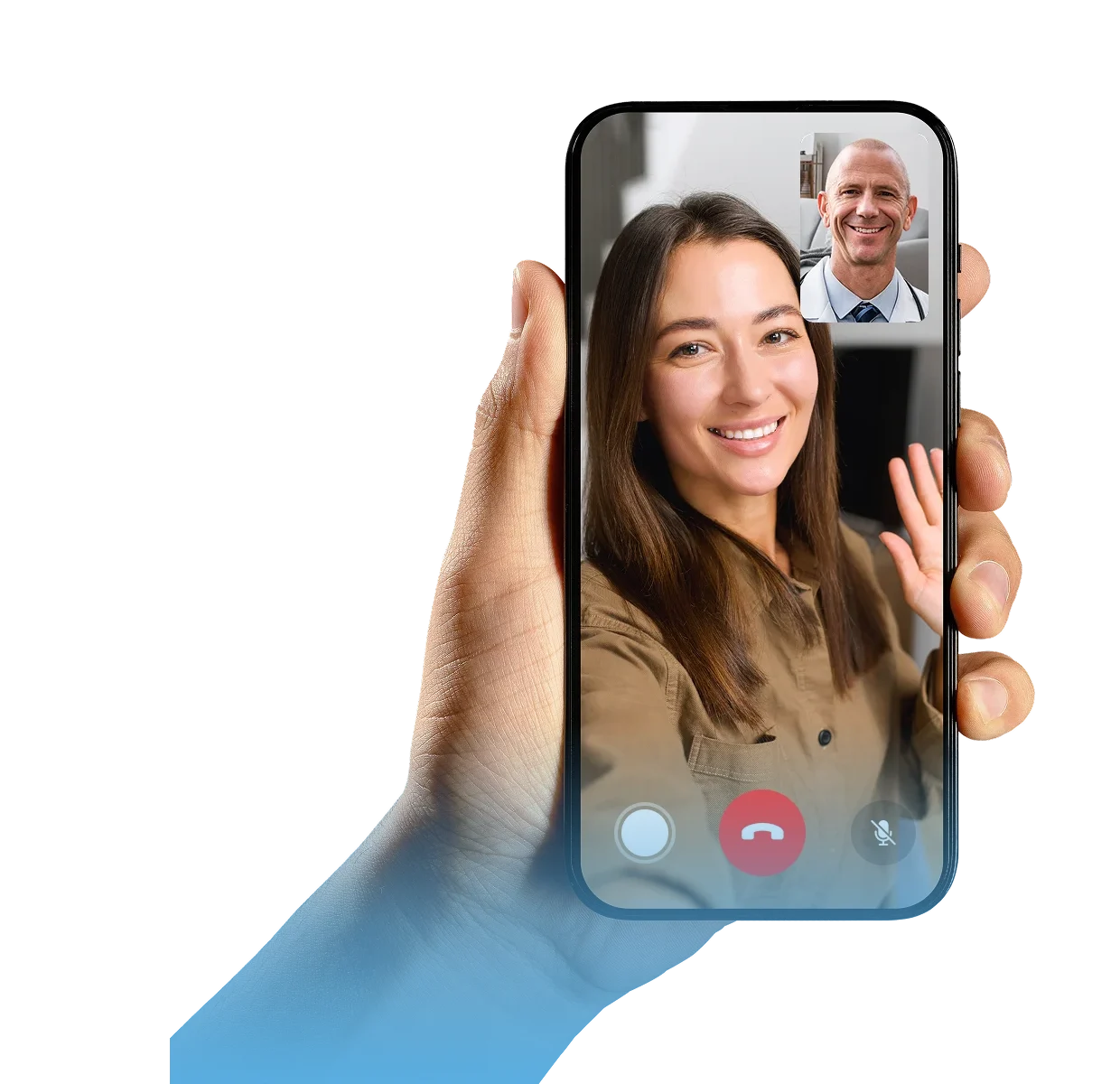
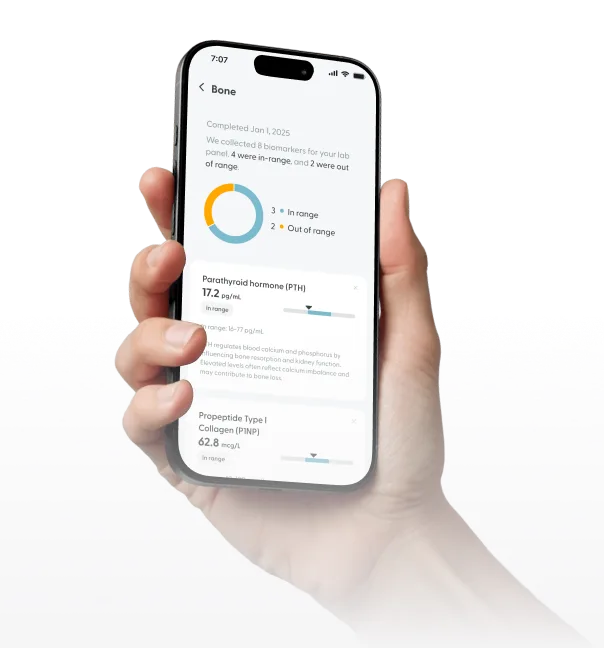
Total Cholesterol

37 mg/mL
In range

LDL (Low-Density Lipoprotein)

47 mg/mL
In range

Triglycerides

158 mg/mL
Above range

A proton pump inhibitor used to treat symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and other conditions involving excessive acid in the stomach.
A histamine-2 blocker (H2-blocker) that works by decreasing the amount of acid the stomach produces, therefore reducing symptoms of heartburn.
Helps strengthen the lower esophageal sphincter and causes the contents of the stomach to empty faster. This allows less time for acid reflux to occur.
“Dr. Puopolo is a very knowledgeable doctor with vast experience in different medical fields. I feel I am in good hands.”
Verified Patient

“Great experience!! Never have done online telehealth before but for sure will again :)”
Verified Patient

“Dr. Culpepper was amazing. He explained things to me that I didn’t understand.”
Verified Patient

“Dr. Sehgal was amazing! Super helpful. She was answering my questions before I even asked. Very happy I picked her.”
Verified Patient

"The appointment went great. It was quick and easy, and the doctor was right on top of things!"
Verified Patient

Reviews shown are from verified LifeMD patients across various services. Photos are for illustrative purposes only.
GERD is a chronic condition, meaning it’s not curable, but it can be managed with appropriate treatment. Treatment options for GERD include lifestyle modifications such as weight loss, avoiding trigger foods, and elevating the head of the bed during sleep. Medications, such as antacids, proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), and H2 blockers, can also be used to reduce the production of stomach acid and relieve symptoms. In some cases, surgery may be recommended for people with severe GERD who do not respond to other treatments.
Untreated or poorly managed GERD can lead to complications, some of which can be serious and even life-threatening. Chronic acid reflux can cause inflammation and scarring of the esophagus, leading to a condition called Barrett's esophagus, which increases the risk of esophageal cancer.
GERD can also cause respiratory problems, such as asthma, and increase the risk of developing pneumonia. In addition, untreated GERD can lead to dental problems, including tooth decay and gum disease. With appropriate treatment and management, however, the risks associated with GERD can be minimized.
GERD is a chronic condition that can last for years or even a lifetime if left untreated. The duration of GERD symptoms can vary from person to person, with some experiencing symptoms only occasionally, while others experience symptoms daily.
The duration of symptoms can also depend on the severity of the condition, with more severe cases requiring longer treatment and management. It’s important to seek medical attention for GERD to prevent complications and improve your quality of life. With appropriate treatment and lifestyle modifications, many people with GERD are able to successfully manage their symptoms and prevent complications.
Yes, GERD can cause shortness of breath. This is the result of stomach acid flowing back up into the esophagus, which can irritate the lining of the esophagus and trigger a reflex that causes the airways to narrow. Coughing and wheezing may occur as well.
In addition, GERD can also cause inflammation in the lungs, which can further contribute to breathing difficulties. If you're experiencing severe shortness of breath or are having difficulty breathing, seek medical attention immediately.
Yes, GERD can cause back pain. This is because the esophagus — and the nerves that surround the esophagus — are located near the spine. So when stomach acid flows back up into the esophagus, it can irritate the nerves and cause pain in the back.
In addition, the muscles in the esophagus may also become strained as a result of frequent acid reflux, which can cause discomfort in the chest and back. It’s important to seek medical attention if you’re experiencing back pain, as this could be a sign of a more serious condition.
Yes, GERD can cause chest pain. When stomach acid flows back up into the esophagus, it can irritate the lining of the esophagus and cause a burning sensation in the chest. This sensation is commonly referred to as heartburn and is a hallmark symptom of GERD.
In addition, GERD can also cause pain in the chest that is similar to that of a heart attack. If you're experiencing chest pain, be sure to seek immediate medical attention.
Studies have suggested that individuals with a family history of GERD may be at a higher risk of developing the condition, although the specific genetic factors that contribute to this risk are not yet fully known. However, some factors such as being overweight or obese, smoking, and taking certain medications, can also play a significant role in the development of GERD. If you have a family history of GERD, it’s a good idea to speak with a healthcare provider about lifestyle modifications that can help reduce your risk of developing the condition.

Family Medicine
4.93 stars 170 reviews


Internal Medicine
4.98 stars 178 reviews


Internal Medicine
4.92 stars 261 reviews


Family Medicine
4.94 stars 178 reviews


Hormone Specialist
4.92 stars 163 reviews
